Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that affects millions of people worldwide, and allergic asthma is one of its most prevalent forms. Allergic asthma is characterized by airway inflammation and constriction triggered by exposure to allergens such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, or mold. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and diagnosis of allergic asthma is crucial for effective management and improved quality of life for those affected.
**Causes of Allergic Asthma:**
Allergic asthma is primarily triggered by an immune system overreaction to specific allergens. When exposed to these triggers, the immune system releases chemicals such as histamine, which inflame the airways and cause symptoms like wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath. Genetic predisposition and environmental factors also play significant roles in the development of allergic asthma.
**Symptoms of Allergic Asthma:**
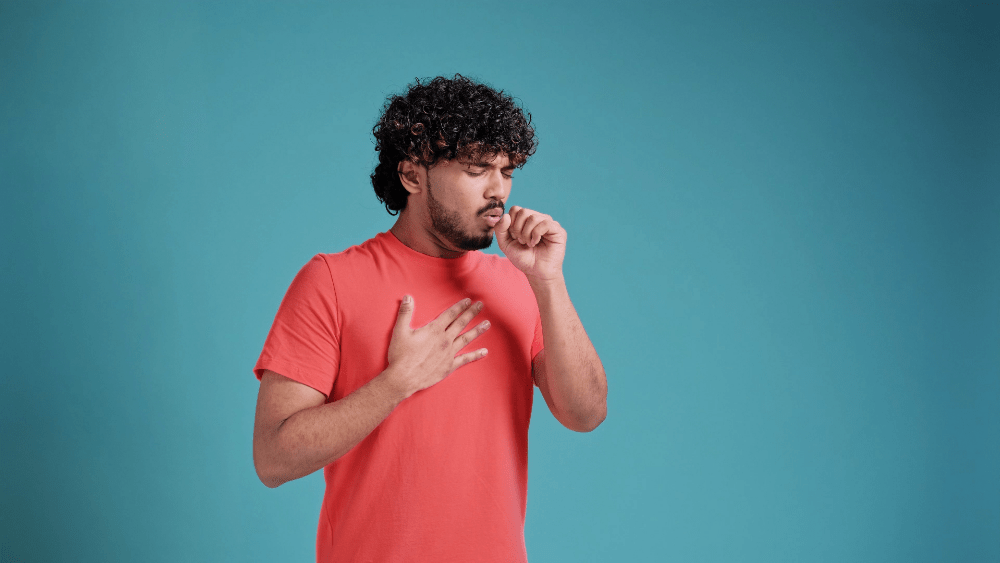
The symptoms of allergic asthma can vary in severity and frequency from person to person. Common signs include:
1. Wheezing: A high-pitched whistling sound when breathing.
2. Coughing: Especially at night or early morning.
3. Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity.
4. Chest tightness: A feeling of pressure or discomfort in the chest.
5. Difficulty sleeping due to coughing or wheezing.
These symptoms may worsen with exposure to allergens, respiratory infections, or during periods of high air pollution.
**Diagnosis of Allergic Asthma:**
Diagnosing allergic asthma typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Key steps in the diagnostic process include:
1. **Medical History:** Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms, triggers, and any family history of asthma or allergies.
2. **Physical Examination:** A thorough examination of the chest and lungs to assess breathing patterns and listen for abnormal sounds like wheezing.
3. **Lung Function Tests:** These tests, such as spirometry and peak flow measurement, evaluate how well your lungs are functioning and help confirm an asthma diagnosis.
4. **Allergy Testing:** Skin prick tests or blood tests can identify specific allergens that may be triggering your asthma symptoms.
Once diagnosed, allergic asthma can be managed through a combination of medication, avoidance of triggers, and lifestyle modifications. Treatment options may include inhaled corticosteroids, bronchodilators, allergy medications, and immunotherapy (allergy shots) for severe cases.
In conclusion, allergic asthma is a prevalent form of asthma characterized by airway inflammation triggered by exposure to allergens. Recognizing the causes, symptoms, and diagnostic methods is essential for effectively managing this chronic condition and improving the quality of life for those affected. If you suspect you may have allergic asthma or are experiencing symptoms, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment.